The Body
EFFECTS OF PATHOGEN/ORGANISMS ATTACK ON THE HUMAN BODY
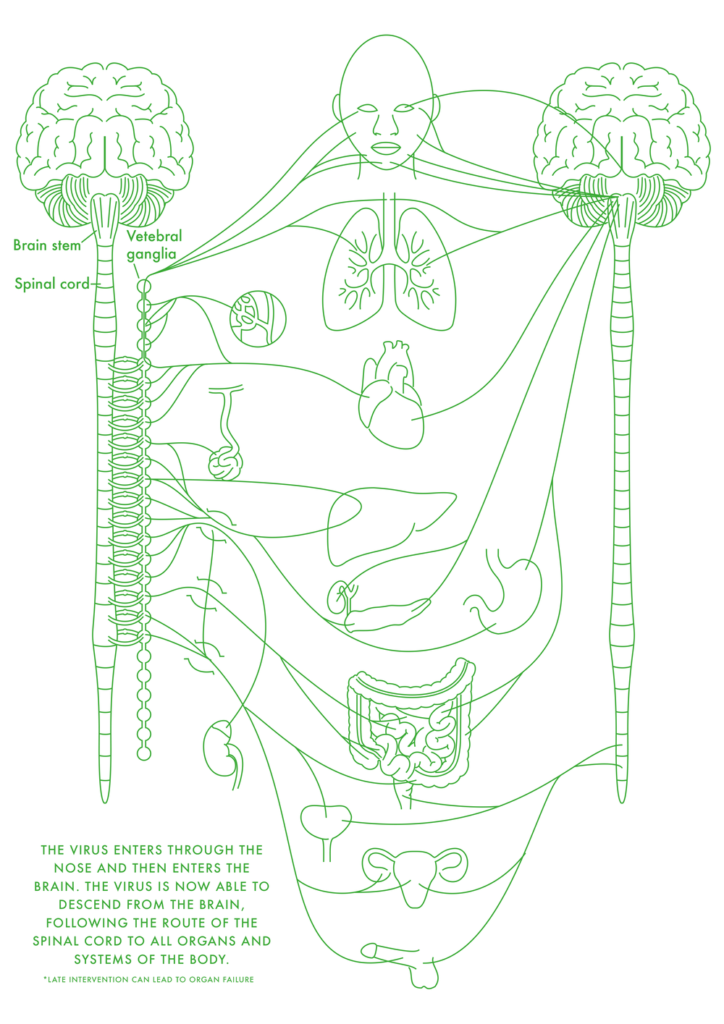
When a pathogen/organism enters the body and the immune system is compromised, replication takes place. They invade, grow and spread locally into tissues and cells. When kept untreated they can invade the blood vessels and cause infection in the bloodstream which can lead to cytokines storm, microthrombosis and organs failure.
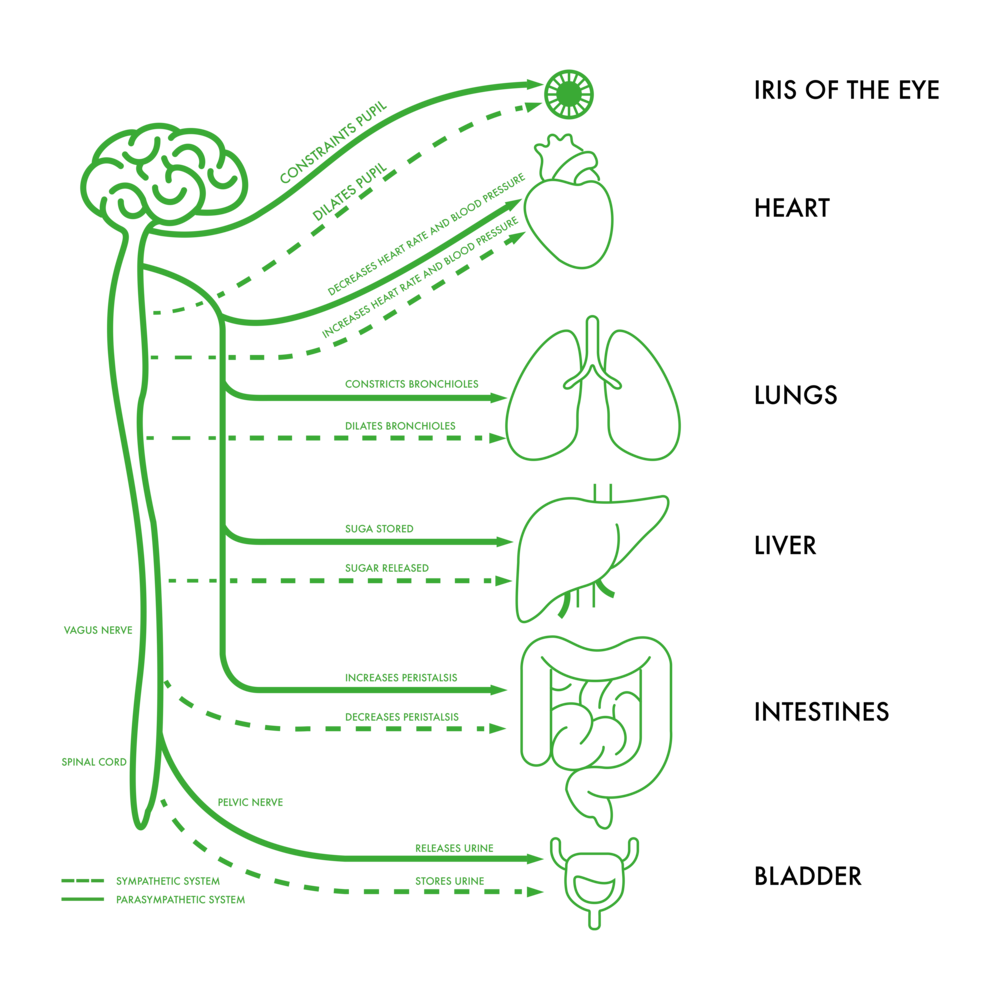
THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
The autonomic nervous system regulates the blood pressure and breathing rates. The system works without a person’s conscious effort. Autonomic nervous system disorders can affect any part of the body. The disorders can be progressive and reversible. The autonomic nervous system controls the internal organs through sympathetic or parasympathetic division nerve fibers, to the brain, pupils, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, bladder, stomach, intestine, digestive glands, salivary, sweat, digestive glands and genitals.
Regulates functions such as:
- Circulation
- Breathing
- Digestion
- Body temperature
- Metabolism
- Water balance and electrolytes
- Excretion
- Urination
- Hormone production
- Sexual response
Vital life force
- Eyes
- Heart
- Lungs
- Adrenal glands/kidneys
- Large and small intestines
- Urinary
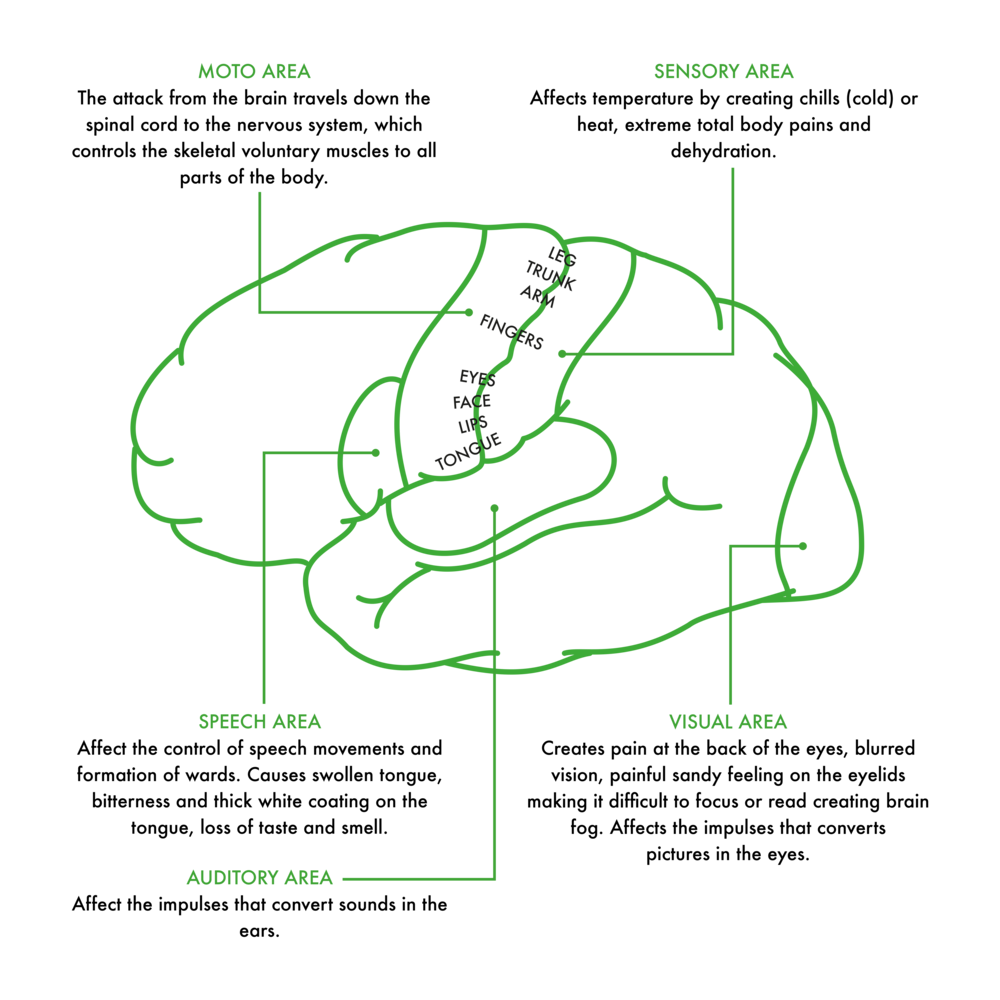
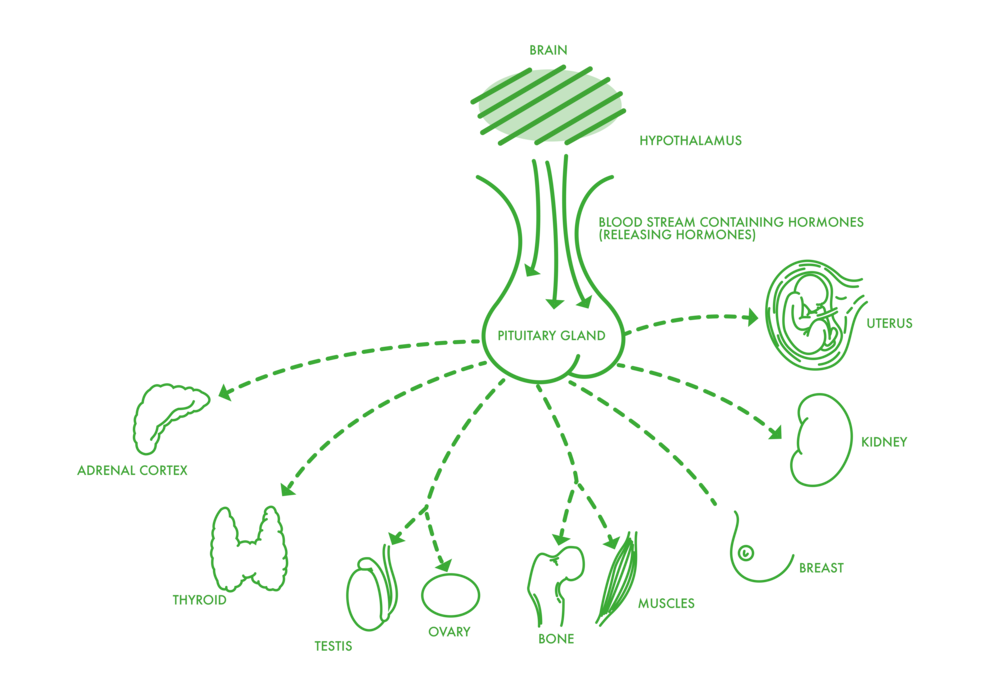
DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE BRAIN
- Hypothalamus
- Blood stream and brain steam
- Pituitary gland
THE NEED TO TREAT THE BODY AS A WHOLE AND NOT IN ISOLATION
There are about 16 systems of the body and each system plays a vital role in the body and is connected. Jobe Health’s detox program is designed to detoxify the body as a whole. Everything in the body is interconnected, which means everything on the outside is a direct reflection of what’s going on the inside. Therefore it is clear that our body has a self-regulating system and cannot be treated in isolation, what affects one organ also affects the other. As in nature, so it is in the body. What affects one system affects the whole body.
SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS OF THE BODY
Digestive system: processes food into nutrients and energy for the body to use and gets rid of waste.
Renal system and excretory system: filters and removes waste & extra fluid through the kidneys. It also controls blood pressure, makes red blood cells, keeps bone health and controls pH levels whilst keeping essential substances in the blood.
Lymphatic system: removes fluid, helps fight against pathogens, working with thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, and lymphatic vessels.
Urinary system: controls water balance within the body, removes waste from the blood.
Endocrine system: secretes hormones, regulates body processes; pineal glands, hypothalamus, pituitary glands, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, testes and ovaries.
Immune system: makes antibodies to fight harmful substances; germs that enter the body through the skin and digestive system.
Respiratory system: removes carbon dioxide from the body, delivers oxygen to blood, lungs and other organs.
Nervous system: processes sensory information to and from the brain, activates body response to the brain, spinal cord and periphery nerves.
Circulatory system: controls the cardio vascular system; together supplying body/organs with oxygen and nutrients.
Muscular system: enables movement with skeletal system. Also helps maintain body temperature, skeletal muscles and tendons.
Skeletal system: supports the body, enables movement with muscular system cartilage, bones, and joints. Integumentary system: includes internal body structures and sensory receptors, hair, skin and nails.
Reproductive system: produces sex hormones and gametes to procreate.
THE NEED FOR HIGH FIBRE PREBIOTIC FOOD FOR YOUR MICROBIOME
What is fibre?
Dietary fibre is known as roughage, it’s the part of the plant food your body can’t digest or absorb, it passes through your body unlike fat, proteins and carbohydrates which your body break down and absorb. This process cannot be carried out without the digestive juices such as hydrochloric acid and bile from the liver. Soluble fibre can be found in oat, peas, apples, citric fruits, carrots barley and psyllium. Insoluble fibre is the type of fibre that keeps thing moving through digestive system and increases stool bulk. Insoluble fibre can be found in whole wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, vegetables such as cauliflower, green and sweet potatoes.
ADDITIONAL BENEFITS OF FIBRE
- Normalises bowel movement.
- Softens and increases the size and weight of your stools making it easier to pass.
- Solidify watery stool and absorbs water by adding bulk to stool
- Helps maintain immune health.
- Lowers the risk of developing haemorrhoids and small pouches in the colon (diverticular disease).
- Stops fermentation in the colon.
- Lowers the risk of colon cancer.